UPHIA 2020-2021: Key Findings*
%
Annual HIV incidence among adults
%
HIV prevalence among adults
%
Viral load suppression among adults living with HIV*
95-95-95 among adults living with HIV
0%
Adults living with HIV who knew their HIV status
0%
Adults who were aware of their HIV status who were on ART
0%
Adults who were on ART who had viral load suppression
RUPHIA 2021: Key Findings**
%
HIV prevalence among adults
%
Viral load suppression among adults living with HIV*
95-95-95 among adults living with HIV
0%
Adults living with HIV who knew their HIV status*
0%
Adults who were aware of their HIV status who were on ART*
0%
Adults who were on ART who had viral load suppression*
**This estimate was based on a denominator between 25 and 49 and should be interpreted with caution.
*UPHIA 2016-2017 Summary Sheet and Final Report, as well as related reports and publications, can be found below.
Related Resources
No results found.
Recent PHIA News
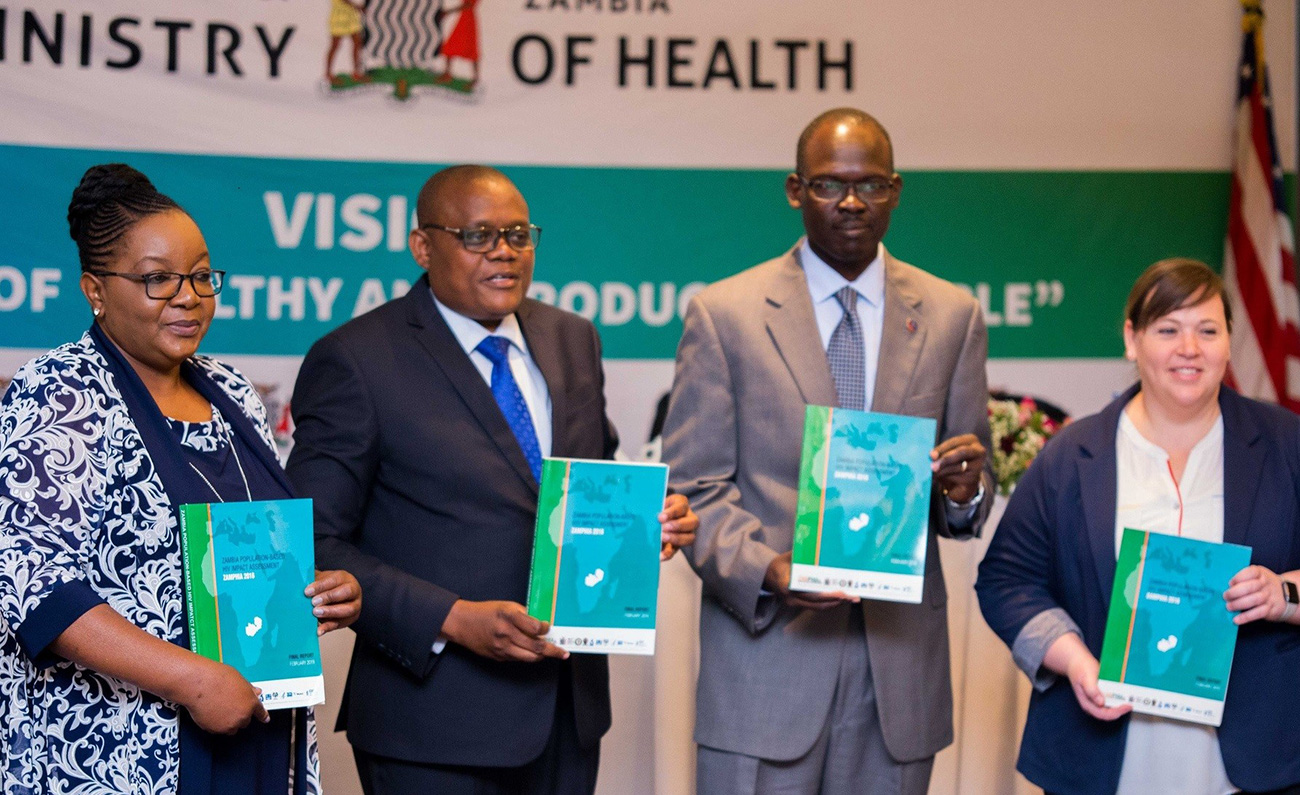

On February 28, 2019, representatives from the Government of Zambia, the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and ICAP at Columbia University gathered
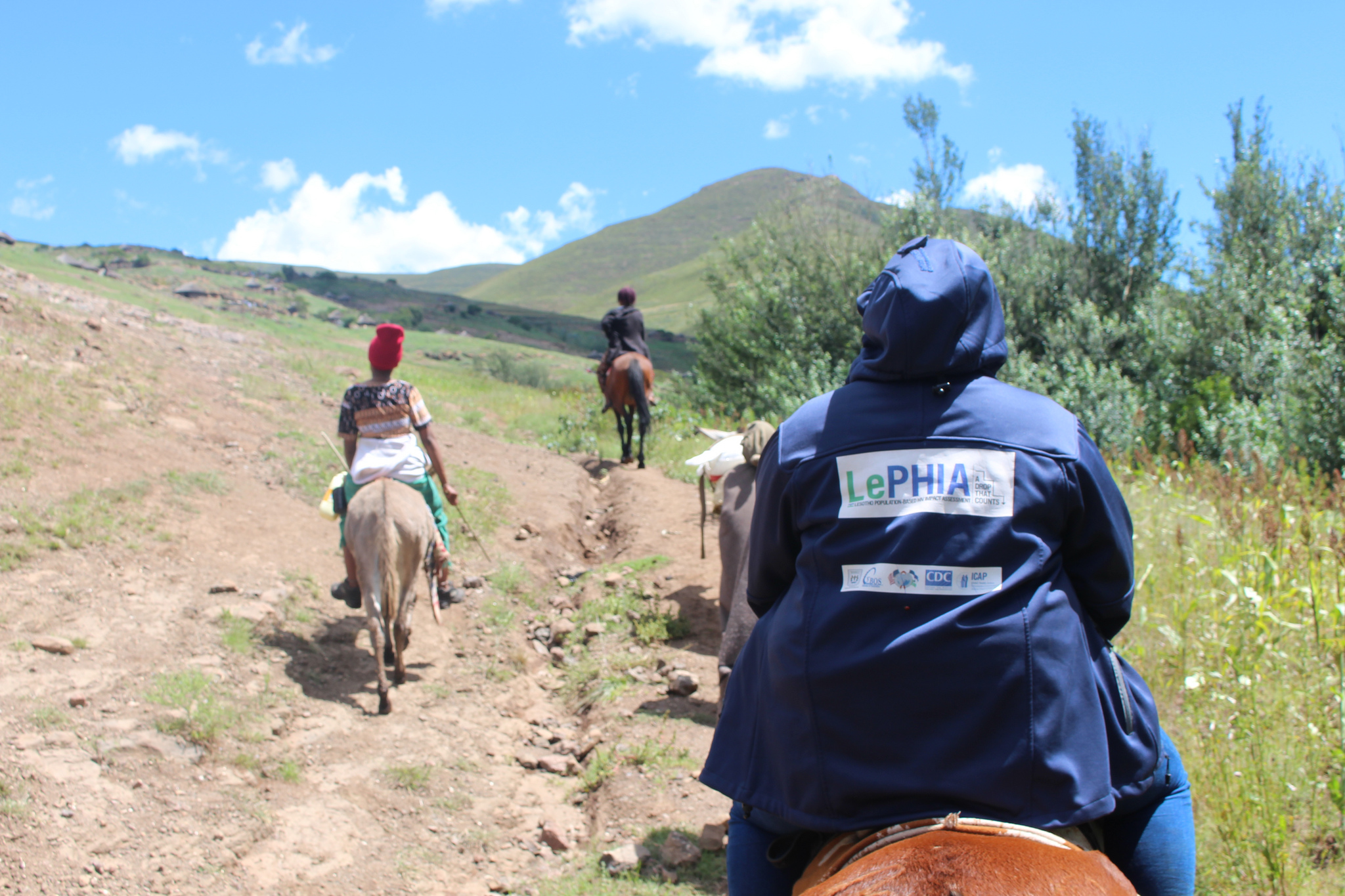

There is a direct link between climate change and public health in Lesotho, according to findings from the Lesotho Population-Based HIV Impact Assessment (LePHIA).
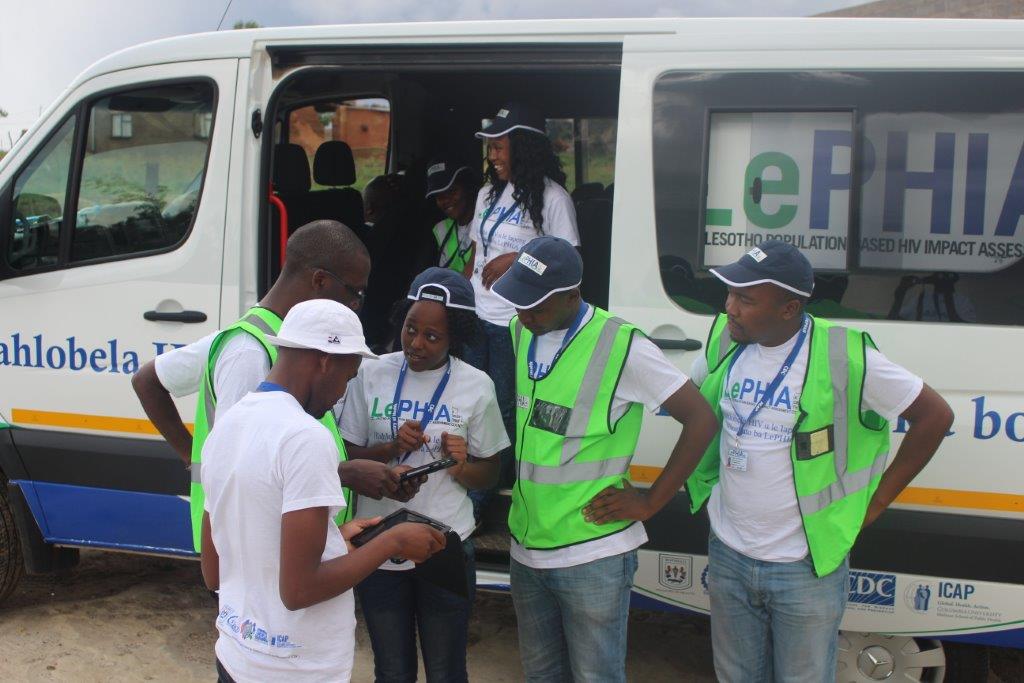

January 16, 2019, Maseru – Today, the Government of Lesotho, the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and ICAP at Columbia University (ICAP) announced the final results of the Lesotho Population-based HIV Impact Assessment (LePHIA) survey.
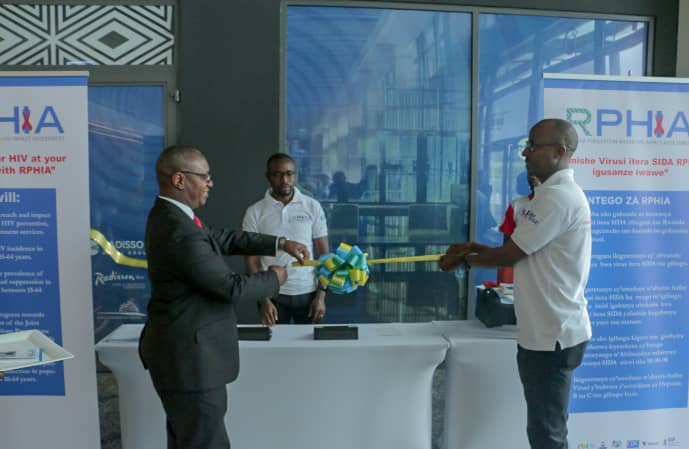

The Ministry of Health announced today the launch of the Rwanda Population-based HIV Impact Assessment (RPHIA).